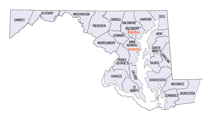
Maryland Counties
There are twenty-four counties and county-equivalents in Maryland. Though an independent city rather than a county, the City of Baltimore is considered the equal of a county. The last new county formation in Maryland occurred when Garrett County was formed in 1872 from portions of Allegany County.Baltimore County, Maryland
Baltimore County Education, Geography, and History
Baltimore County is a county located in the northern part of the state of Maryland. Based on the 2010 census, the population was 805,029,
making it the third-most populous county in Maryland. Its county seat is in Towson, in the north-central section just north of the adjacent
City of Baltimore.
Baltimore County is included in the Baltimore-Columbia-Towson, MD Metropolitan Statistical Area, which is also included in the
Washington-Baltimore-Arlington, DC-MD-VA-WV-PA Combined Statistical Area. It is increasingly part of the East Coast "megalopolis" stretching
from Boston to Richmond.
Etymology - Origin of Baltimore County Name
The name of the County was derived from the barony of the Proprietor of the Calverts' new colony in the Province of Maryland, Cecil Calvert, 2nd Baron Baltimore, (1605-1675),, and the town of "Baltimore" in County Cork, of southern coastal Ireland.
Demographics:
County QuickFacts: CensusBureau Quick Facts
Baltimore County History
The earliest known documentary record of the county politically in the Maryland State Archives in the Hall of Records in the state capital
of Annapolis is January 12, 1659, when a writ was issued on behald of the General Assembly of Maryland to its sheriff and is considered by
historians to be its official year of "erection" (founding/establishment date) among the now twenty-three counties of the State, as it assumes
that a certain amount of organization and appointments in the middle 17th Century had already occurred. Previously, Old Baltimore County was
more known as a geographical entity than a political one, with its territorial limits consisting of most of northeastern Maryland, then the
northwestern frontier of the Province and included the present day jurisdictions of Baltimore City, Cecil, and Harford Counties, as well as
parts of Carroll, Anne Arundel, Frederick, Howard, and Kent Counties. In 1674, a proclamation of the Proprietor, established the then
extensive boundary lines for old Baltimore County. Over the next century, various segments of the Old County were sliced off as population and
settlements increased in the fringe regions so as to have a shorter distance to newly established county seats with their courts and
commercial businesses.
In 1674, a portion of northeastern Baltimore County, as well as a portion of northwestern Kent County, was split off to erect Cecil County. In
1748, a portion of western Baltimore County, as well as a portion of Prince George's County to the south, were split off to erect Frederick
County. In 1773, Harford County to the east was split off from Baltimore County. In 1837, another part of western Baltimore County was
combined with a part of eastern Frederick County to erect Carroll County. After the adjustment of the County's southern boundary with Anne
Arundel County stated to be the upper Middle and Western Branches of the Patapsco River in XXXX, a portion of its northwestern area was
designated in 1838 as the "Western District" or "Howard District" of Arundel and in 1851 was officially separated to form the new Howard
County (named for Revolutionary War commander of the "Maryland Line" of the Continental Army, Col. John Eager Howard, [1752-1827]).
The separation of Baltimore County from Baltimore City which it surrounds on three sides (east, north and west) occurred on July 4, 1851, as a
result of the adoption of the 1851 second state constitution. Towsontown was voted in a referendum by the voting citizens as the new
"county seat" several years later on February 13, 1854. A new Baltimore County Courthouse was authorized to be built facing Washington Avenue,
between Chesapeake and Pennsylvania Avenues to replace the previous courthouse and governmental offices then centered for near 85 years in the
City, which had been the official "county seat" since just before the American Revolution.
Geography: Land and Water
As reported by the Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 682 square miles (1,770 km2), of which 598 square miles (1,550 km2) is
land and 83 square miles (210 km2) (12%) is water. It is the third-largest county in Maryland by land area. The larger portion of the terrain
is undulating, with bold hills often rising to a height of 800 feet (240 m) above tide water. The highest elevation is approximately 960 feet
(290 m) above sea level, along the Pennsylvania state line near Steltz. The lowest elevation is sea level along the shoreline of the
Chesapeake Bay.
Much of Baltimore County is suburban in character, straddling the border between the Piedmont plateau to the northwest and, in the southern
and southeastern regions of the county bordering the Patapsco River and the Chesapeake Bay, the Atlantic coastal plain. Northern Baltimore
County is primarily rural, with a landscape of rolling hills and deciduous forests characteristic of the Southeastern mixed forests and shares
the geography with its neighbors to the east and west, Carroll County and Harford County, and going north across the historic Mason-Dixon line
into Adams County and York County in south central
Neighboring Counties
Bordering counties are as follows:
- North: York County, Pa.
- East: Harford County
- Southeast: Chesapeake Bay
- South: Anne Arundel County; Baltimore city
- Southwest: Howard County
- West: Carroll County
Education
Colleges and universities
The University System of Maryland maintains two universities in Baltimore County:
- Towson University in Towson, (founded 1866 as Maryland State Normal School in Baltimore City; renamed Maryland State Teachers College at Towson, 1935; Towson State College, 1963; Towson State University, 1976, Towson University, 1997).
- University of Maryland, Baltimore County in Catonsville, founded 1966.
There are also two private colleges in Baltimore County:
- Goucher College (in Towson), founded as Women's College of Baltimore, 1885; located on Saint Paul Street and 23rd Streets.
- Stevenson University, formerly Villa Julie College (campuses in Stevenson and Owings Mills).
Other schools having a campus in Baltimore County:
- Loyola College in Maryland (in Hunt Valley, main campus in Baltimore at North Charles Street and East Cold Spring Lane, [formerly Loyola College, founded 1852]).
- The Community College of Baltimore County (CCBC), with campuses in Catonsville, Essex, and Dundalk.
Public schools
All public schools in Baltimore County are operated by Baltimore County Public Schools, with the exception of the Imagine Me Charter School which opened August 2008.
Private schools
Baltimore County has a number of private schools at the K-12 grade levels.