Utah Geography: The Land
Geography and Landforms of Utah
 Find
an overview of Utah geography, topography, geographic land regions, land areas, and major rivers.
Find
an overview of Utah geography, topography, geographic land regions, land areas, and major rivers.
Access Utah almanac furnishing more details on the state geography, geographical and land regions, climate and weather, elevation, land areas, bordering states, and other statistical data.
Utah is bordered by Idaho and Wyoming on the north and by Arizona on the south. On the east, Utah is bordered by Colorado. On the west, Utah is bordered by Nevada.
Major rivers in Utah include the Colorado River
and the Green River.
Utah is divided into the three main geographic regions listed below.
- Rocky Mountains
- Colorado Plateau
- Basin and Ridge Region
Utah Highest, Lowest, & Mean Elevations |
|
|---|---|
| Mean Elevation | 6,100 ft. |
| Highest Point | Kings Peak 13,528 ft. |
| Lowest Point | Beaverdam Wash 2,000 ft. |
Utah Land Area (Square Miles) |
|
| Geographic Center | In Sanpete County, 3 mi. N. of Manti Longitude: 111° 41.1'W Latitude: 39° 23.2'N |
| Total Area | 84,898.83 sq. mi. 13th |
| Land Area | 82,143.65 sq. mi. 96.76% |
| Water Area | 2,755.18 sq. mi. 3.24% |
| Forested Land Area | 29.9% |
| Dimensions (Length - Width) |
350 miles - 270 miles |
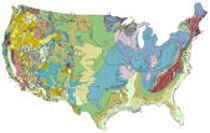
Utah: Physiographic Regions
Three primary physiographic regions, each with unique topographic, geologic, and geomorphic characteristics, extend into Utah. They include the
- Colorado Plateau,
- the Basin and Range, and the
- Middle Rocky Mountains.
Rocky Mountains
Rocky Mountains: Running north to south through the United States, the Rocky Mountains are an imposing presence in many of the western states. In Utah, two ranges of the Rockies extend through the northeast corner of the state; the Uinta Range and the Wasatch Range.
The Uinta Range extends from Colorado in the east almost all of the way to Salt Lake City in north central Utah. It is the only range of the Rocky Mountains that runs east and west. Lakes and flat-bottomed canyons, formed by glacial activity, are interspersed with mountains that reach over 13,000 feet above sea level. Kings Peak, the highest point (13,528 feet above sea level) in Utah, is found in the Uinta Range.
The Wasatch Range stretches from Mount Nebo in north central Utah northward into Idaho. On the west, the mountains range from 6,000 to 8,000 feet above sea level.
Colorado Plateau
The Colorado Plateau is centered on the four corners area and extends into Colorado, Utah, Arizona, and New Mexico. It is an area of tablelands with moderate to high relief dissected by narrow and widely-spaced stream valleys. The Colorado Plateau is characterized by limited precipitation, cold winters and hot summers. Lowest elevations are covered with arid shrublands with grass interspersed. Sagebrush is dominant over large areas, with cottonwoods along perennial water courses. At moderate elevations, woodland vegetation is dominated by pinyon pine and juniper, with various shrubs intermixed. Montane forest is in high elevations, with ponderosa pine and Douglas fir dominant to the south and lodgepole pine and aspen farther north.
Most of the southern and eastern areas of Utah are made up of the Colorado Plateau. This area has high country cut by deep canyons and valleys. To the west part of the region is high plateaus such as Aquarius, Fish Lake, and Markagunt. These are more than 11,000 feet above sea level. In the east the Colorado passes through Utah with the Henry Mountains to the west banks of the river and to the east are the Abajo and La Sal mountains. Bryce Canyon, Cedar Breaks Canyon, and Zion Canyon are all found in the Colorado Plateau area.
"Four Corners", is the only place in the United States where four states meet. Utah's southeastern corner meets the corners of Arizona, New Mexico, and Colorado.
Basin and Ridge Region
The Basin and Range is a large physiographic area covering most of Nevada, part of eastern California, western Utah, and southeast Idaho. It lies in the rainshadow of the Sierra Nevada, south of the Columbia Plateau and north of the Mohave Desert, and is a mosaic of xeric basins, scattered mountains, and salt flats. It is hotter and contains more and higher mountains than the Columbia Plateau, with more perennial streams and ponderosa pine forest at the higher elevations. Compared to the Mojave Desert, it is not as hot and is more dominated by shrubland and less by grassland.
The Basin and Ridge Region is one of the driest areas of the United States. It covers several states including Utah. Covered by small mountains and basins except on the east and west edges where the mountains are higher this region is in the western part of the state. The Great Salt Lake is located in the northeastern corner of the Basin and Ridge Region and the Great Salt Lake Desert is located to the west and southwest of the lake. Located in the center of the Great Salt Lake Desert is about 4,000 acres of hard flat salt beds. The Bonneville Salt Flats are named after the ancient sea that covered the area, Lake Bonneville.
The area located in the extreme southwestern corner of the Basin and Ridge Region is the warmest and lowest part of the state is know as "Utah's Dixie".
Utah Landscape and Landforms:
Mojave Desert
In the "Great American Desert" of the Southwest, the Mohave lies between and is intermediate in nature between the Great Basin to the north and the Sonoran Desert to the south and east. It is mostly in southeast California but extends also into southern Nevada, northwest Arizona, a very small part of southwest Utah, and lies in the rainshadow of the Southern California Ranges to the west. Its most prominent features are broad, sparsely vegetated plains. However, it also includes dry lakes, sharply rising buttes and relatively small mountain ranges, and its eastern portion is cut through by the Colorado River. It is generally a higher elevation desert than the Sonoran, although elevation descends to -300 m in Death Valley. Low precipitation, most falling in winter, with low winter and high summer temperatures are characteristic.
Utah Mountains
These north-to-south lying mountains are centered in Utah and extend slightly into Wyoming and Idaho. They consist of the Wasatch and Uinta Ranges and separate the Great Basin from the Colorado Plateau. The four primary vegetation types reflect elevation and are similar to those in the Southern Rockies. Alpine tundra tops the highest areas, and a subalpine fir and Englemann spruce zone lies below that. Both the subalpine zone and the next lower zone, a montane area dominated by Douglas fir and ponderosa pine, can be converted by fire into lodgepole pine or aspen stands. Pine in the montane zone is often underlain by sagebrush and grasses. The fourth and lowest zone is a woodland dominated by mountain-mahogany, scrub oak, or pinyon-juniper.
Wyoming Basin
As its name suggests, the Wyoming Basin is primarily in Wyoming but also extends into northern Colorado, southern Montana, and very small parts of northeast Utah and southeast Idaho. The area consists of broad intermountain basins interrupted by isolated hills and low mountains that merge to the south into a dissected plateau. It is basically a shrubsteppe, dominated by sagebrush and shadscale, interspersed with areas of shortgrass prairie. Higher elevations are in mountain shrub vegetation, with coniferous forest atop the highest areas.