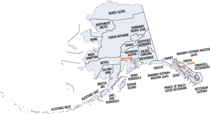
Alaska Boroughs
Alaska is divided into nineteen organized boroughs and one "Unorganized Borough." The Borough Act of 1961 created "The Unorganized Borough" including all of Alaska not within a Unified, Home rule, First class or Second class Borough. The newest borough is Petersburg incorporated after voters approved borough formation in December 2012. Alaska and Louisiana are the only states that do not call their first-order administrative subdivisions counties (Louisiana uses parishes instead)City and Borough of Sitka, Alaska
Sitka Borough Education, Geography, and History
The City and Borough of Sitka, formerly New Archangel while under Russian rule , is a unified city-borough located on Baranof Island and the southern half of Chichagof Island in the Alexander Archipelago of the Pacific Ocean (part of the Alaska Panhandle), in the state of Alaska. The borough seat of Sitka is the city of Sitka. The population of Sitka Borough is 8,881. The borough was formed in 1971. Sitka named from Tlingit word Shee At'ik? meaning "People on the outside of Shee (Baranof Island)."
Etymology - Origin of City and Borough of Sitka Name
The name Sitka (derived from Sheet'ká, a contraction of the Tlingit name Shee At'iká) means "People on the Outside of Shee," Sheet'-ká X'áat'l (often expressed simply as Shee) being the Tlingit name for Baranof Island. The town is often referred to as "Sitka-by-the-Sea."Demographics:
County QuickFacts: CensusBureau Quick Facts
History of Sitka Borough History, Alaska
The area was originally established by the native Tlingit (Kolosh) Indians. Old Sitka was founded in 1799 by Alexandr Baranov, the governor of Russian America. Baronov arrived under the auspices of the Russian-American Company, a "semi-official" colonial trading company chartered by Tsar Paul I. In 1802 a group of Tlingit destroyed the original establishment (an area today called the "Old Harbor") and massacred most of the Russian inhabitants. Baranov was forced to levy 10,000 rubles in payoff for the safe return of the surviving settlers. The new Russian palisade atop "Castle Hill" (Noow Tlein) that surrounded the Governor's Residence had three watchtowers, armed with 32 cannon, for defense against Tlingit attacks.
Baranov returned to Sitka in 1804 with a large contingent of Russians and Aleuts aboard the Russian warship Neva. The ship bombarded the natives' village, forcing the Tlingits to run away into the surrounding forest. Following their victory at the Battle of Sitka the Russians established a stable settlement in the form of a fort, named "Novo-Arkhangelsk" (or "New Archangel," a reference to the largest city in the region where Baranov was born). In 1808, with Baranov still governor, Sitka was designated the capital of Russian America.
The Sitka Lutheran Church, built in 1840, was the first Protestant church on the Pacific Coast. The Russian Orthodox Cathedral of St. Michael was founded in 1848, and St. Peter's by-the-Sea Episcopal Church was consecrated as "The Cathedral of Alaska" in 1900. A list of all twenty of the buildings and sites in Sitka that appear in the National Register of Historic Places can be found here or here.
Sitka was the site of the ceremony in which the Russian flag was lowered and the United States flag raised after Alaska was purchased by the United States in 1867 after the sea otter pelt trade died out. The flag lowering and raising event is re-enacted in Sitka every October 18 (Alaska Day). After the original ceremony, the entire US government presence in Alaska until the Klondike Gold Rush consisted of a single customs inspector on the island. Sitka would serve as the capital of the Alaska Territory until 1906, when the seat of government was relocated north to Juneau. The state's first newspaper, The Sitka Times, was published by Barney O. Ragan on September 19, 1868.
While gold mining and fish canning paved the way for the towns initial growth, it wasn't until World War II, when the Navy constructed an air base on Japonski Island, (with its 30,000 service personnel) that Sitka finally came into its own. Today Sitka encompasses portions of Baranof Island and the smaller Japonski Island (across the Sitka Channel from the town), which is connected to Baranof Island by the O'Connell Bridge. Japonski Island is home to Sitka Rocky Gutierrez Airport (IATA: SIT, ICAO: PASI), the Sitka branch campus of the University of Alaska Southeast, the Mt. Edgecumbe High School - a state-run boarding school for rural Alaskans, the Indian Health Service regional hospital SEARHC (South East Alaska Regional Healthcare Center), a US Coast Guard air station, and the port and facilities for the USCGC Maple (WLB-207).
The waters around Sitka are famous for the presence of large populations of humpback whales, which sometimes breach and spin before crashing back to the water. Each November the town celebrates "Whale Fest" at the peak of the October-January southern migration of the 40-ton cetaceans, the greatest in Southeast Alaska. Nearby St. Lazaria Island, a seabird haven (part of the Alaska Maritime National Wildlife Refuge) is a home to puffins, petrels, and many other birds
Geography: Land and Water
As reported by the Census Bureau, the borough is the largest incorporated city by area in the US, with a total area of 4,811
square miles (12,460.4 km2), of which 2,870 square miles (7,400 km2) is land and 1,941 square miles (5,030 km2) (40.3%) is water. The non-city
Alaskan borough of North Slope Borough is the largest incorporated area in the US
Sitka displaced Juneau, Alaska as the largest incorporated city in the United States upon the 2000 incorporation with 2,874 square miles
(7,440 km2) of incorporated area. Juneau's incorporated area is 2,717 square miles (7,040 km2). Jacksonville, Florida, is the largest city in
area in the contiguous 48 states at 758 square miles (1,960 km2).
Neighboring Boroughs:
- Skagway-Hoonah-Angoon Census Area, Alaska - northeast
- Wrangell-Petersburg Census Area, Alaska - southeast
Education