Michigan Geography: The Land
Geography and Landforms of Michigan
 Find an overview of Michigan geography,
topography, geographic land regions, land areas, and major rivers.
Find an overview of Michigan geography,
topography, geographic land regions, land areas, and major rivers.
Access Michigan almanac, furnishing more details on the state geography, geographical and land regions, climate and weather, elevation, land areas, bordering states, and other statistical data.
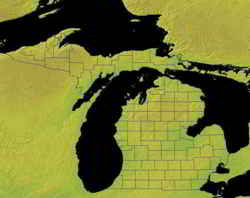
The state of Michigan consists of two peninsulas separated by the Straits of Mackinac. The Upper Peninsula lies between Lake Michigan and Lake Superior. The Lower Peninsula is bordered on the West by Lake Michigan and on the East by Lake Huron, Lake Erie, and two rivers, the Detroit and the St. Clair.
Michigan, one of the leading manufacturing states,
is a leading tourist state as well. Touching on four of the five Great Lakes, the two land areas of Michigan give the state a shoreline of 3,288 miles,
second in length only to Alaska. Michigan also supports over 11,000 lakes. Michigan's two separate land areas are called the Upper Peninsula and the
Lower Peninsula. They're connected by the five mile long Mackinac Bridge.
Michigan Highest, Lowest, & Mean Elevations |
|
|---|---|
| Mean Elevation | 900 ft. |
| Highest Point | Mt. Arvon 1,979 ft. |
| Lowest Point | Lake Erie 572 ft. |
Michigan Land Area (Square Miles) |
|
| Geographic Center | In Wexford County, 5 mi. NNW of Cadillac Longitude: 84° 56.3'W Latitude: 45° 3.7'N |
| Total Area | 96,716.11 sq. mi. 11th |
| Land Area | 56,803.82 sq. mi. |
| Water Area | 39,912.28 sq. mi. 41.26% |
| Forested Land Area | 53.2% |
| Dimensions (Length - Width) |
490 miles - 240 miles |
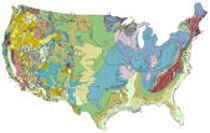
Michigan: Physiographic Regions
The landscape of Michigan comprises the Superior Upland and the Great Lakes Plains.
Superior Upland
The western area of the Upper Peninsula is referred to as the Superior Upland. In the western part of the Upper Peninsula, the land achieves higher elevations and the terrain becomes more rugged. The Superior Upland runs along Lake Superior and into the Porcupine Mountains in northwestern Michigan. Mount Arvon, the highest point in Michigan, is found on the Upper Peninsula.
Great Lakes Plains
The Lower Peninsula is part of the Great Lakes Plains that stretch, along the Great Lakes, from Michigan and Wisconsin to Ohio. The Lower Peninsula
is fairly level but some low rolling hills can be found in the south. To the north this changes to a northern tableland of hilly belts. The lowest
point in Michigan, along the shore of Lake Erie is found in the Lower Peninsula.
Michigan Landscape and Landforms:
Boreal Hardwood Transition
As the name implies, this area is a transition zone between the mixed hardwood forest to the south and the boreal forest to the north. Northern Minnesota, Wisconsin, and Michigan are in this physiographic area, as is much of southern Ontario and a small area of southeast Manitoba. The Great Lakes are a prominent ecological force in this area, affecting microclimates and forest community composition. These forest communities are a heterogeneous matrix with various oaks, maples, birch, and pines representing the southern element and spruces, tamarack, and balsam fir of boreal origin. Aspen is a common early successional species throughout.
Upper Great Lakes Plain
The Upper Great Lakes Plain covers the southern half of Michigan, northwest Ohio, northern Indiana, northern Illinois, southern Wisconsin, and small portions of southwest Minnesota and northwest Iowa. Glacial moraines and dissected plateaus are characteristic of the topography. Broadleaf forests, oak savannahs, and a variety of prairie communities are the natural vegetation types. A "Driftless Area" was not glaciated during the late Pleistocene and emerged as a unique area of great biological diversity.
The Lower Peninsula is fairly level but some low rolling hills can be found in the south. To the north this changes to a northern tableland of hilly belts. The lowest point in Michigan, along the shore of Lake Erie is found in the Lower Peninsula.